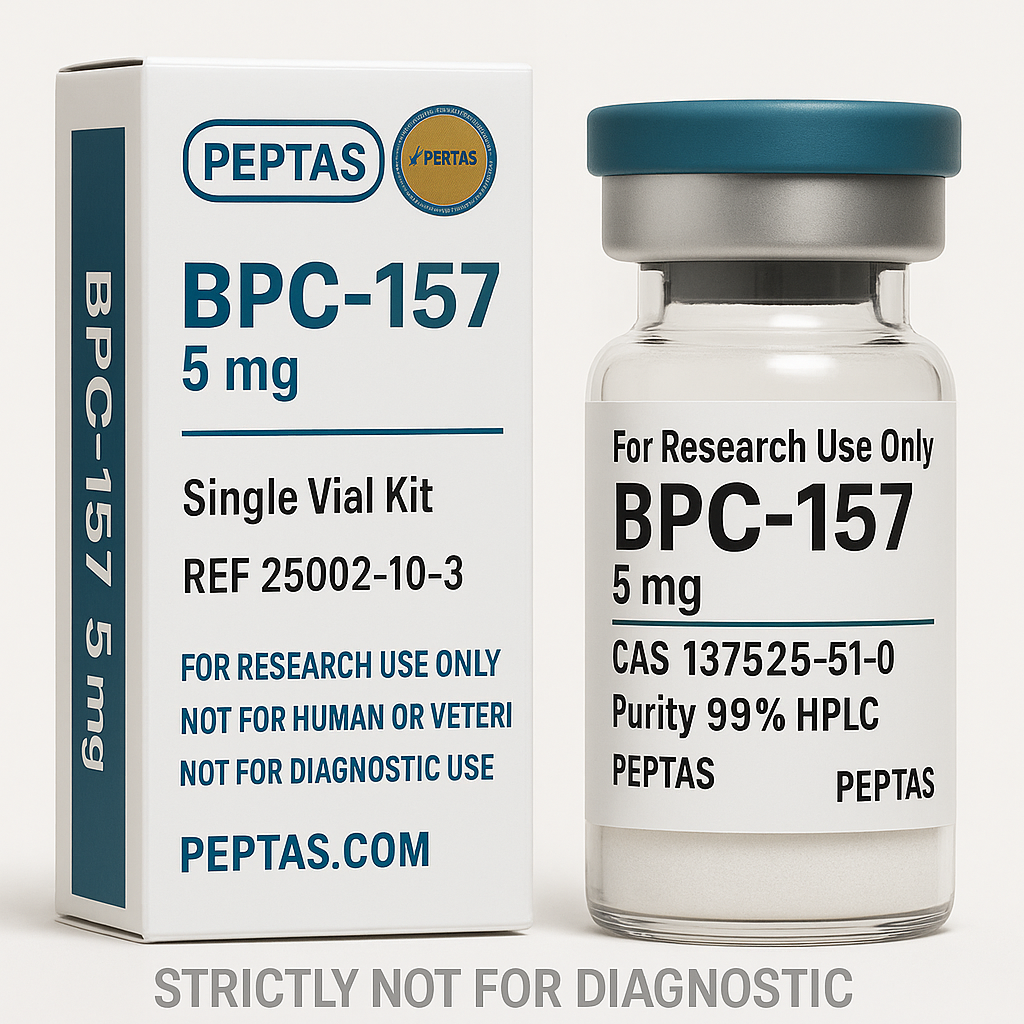
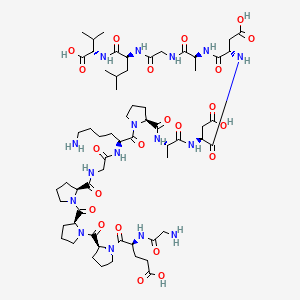
BPC-157 Structure
Source:pubchem
For Research Use Only – Not for Human or Veterinary Use
Product Summary
BPC-157, short for Body Protection Compound 157, is a synthetic peptide originally derived from a naturally occurring compound found in gastric juice. Characterized by its stable 15-amino-acid sequence, BPC-157 has attracted attention from the scientific community for its potential role in supporting tissue repair mechanisms [1]. Although its specific molecular pathways remain under investigation, studies have broadly examined its impact on wound healing, inflammatory modulation, and possibly joint or tendon care.
Key Details
Molecular Formula: C₆₂H₉₈N₁₆O₂₂
Molecular Weight: 1419.55 g/mol
CAS Number: 137525-51-0
Potential Research Applications
1. Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration
- Preliminary in vitro and animal model studies suggest that BPC-157 may influence angiogenic factors, collagen production, and inflammatory responses, supporting comprehensive healing processes [2].
- Gastrointestinal Research
- Owing to its origins in gastric juice, some research explores how BPC-157 might modulate mucosal integrity in the digestive tract, offering a controlled model to study protective factors in gut epithelium [3].
- Tendon and Ligament Investigations
- Scientists have conducted experiments to determine the peptide’s effect on soft tissue recovery, aiming to clarify whether BPC-157 could have a supportive role in tendon or ligament repair.
Safety and Compliance
- Research Use Only
- BPC-157 is not approved for human consumption or therapeutic use. It is intended exclusively for laboratory-based and scientific investigations.
- Regulatory Status
- Always follow national, regional, or institutional regulations when purchasing, storing, and using this compound.
- Liability
- Users assume full responsibility for determining the suitability of BPC-157 in their applications. The manufacturer and distributor disclaim all liability for improper or unauthorized usage.
References
- Sikiric, P. et al. (2011). BPC-157 and Its Regulatory Role in Different Models of Tissue Recovery. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 17(18), 1803–1823.
- Chang, C. H. & Tsai, W. C. (2017). Peptides and Their Role in Wound Healing: Insights from BPC-157 Research. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease, 1863(3), 731–736.
- Boros, M. & Kertesz, D. (2019). Gastroprotective Aspects of Synthetic Peptides: A Focus on BPC-157 in Preclinical Studies. Gastrointestinal Research International, 12(4), 221–229.
Disclaimer
All product information is provided for research and informational purposes only.
BPC-157 is not designated for medical, diagnostic, or therapeutic applications. Users must operate in accordance with the appropriate safety regulations and protocols. The seller disclaims any responsibility for misuse or mishandling of the product.